| |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
A daily bite-size selection of top business content. |
| |
| |
| |
Quote: James Clear - Writer, speaker and researcher - Atomic Habits“If you get one percent better each day for one year, you’ll end up thirty-seven times better by the time you’re done.” — James Clear - Writer, speaker and researcher - Atomic HabitsThis quote encapsulates the power of compounding small improvements—a central theme in modern performance psychology and organisational behaviour. The phrase illustrates how seemingly minor, daily advances in habit or process can result in transformation far beyond what most imagine. Mathematically, a 1% daily improvement, when compounded over 365 days, leads to results nearly 38 times better than the starting point. James Clear uses this insight to shift focus away from sudden, dramatic changes and towards the sustainable, incremental shifts that yield exponential growth over time. This idea forms the core philosophy of his best-selling book, Atomic Habits, which demonstrates that meaningful progress is achieved not through isolated breakthroughs, but through the relentless accumulation of tiny gains—a process available to anyone, every day. About James ClearJames Clear is a leading writer, speaker, and researcher on the science of habits, decision-making, and continuous improvement. Born in Hamilton, Ohio, Clear crafted his own major in biomechanics at Denison University and was a standout student-athlete, experiences that grounded his fascination with performance optimization. After graduating in 2008, Clear turned his attention to writing, launching jamesclear.com to share research-driven insights on behaviour, productivity, and change. His 2018 book, Atomic Habits, rapidly became an international phenomenon:
Clear's work is grounded in synthesis—he draws on biology, neuroscience, psychology, philosophy, and personal experience to offer practical strategies for lasting improvement. Through speaking engagements, workshops, and his widely followed "3-2-1" newsletter, Clear has equipped millions with techniques to make small, actionable shifts that enable compounding, lifelong change. Leading Theorists Related to Small Improvements and CompoundingThe science and strategy of continuous improvement is deeply rooted in both psychology and operational theory. Several key thinkers underpin the philosophy embodied by Clear’s quote:
James Clear’s message thus stands not only on popular intuition but on an interlocking foundation of behavioural science, Eastern and Western management theory, and real-world sports and business excellence. His quote distils the timeless truth: small choices, if compounded, drive extraordinary change.
|
| |
| |
Term: KaizenKaizen is a foundational philosophy and practice in operations and management, defined as a system of continuous improvement through small, incremental changes. The term is derived from two Japanese words: “kai” (change) and “zen” (good), meaning “good change” or improvement—but in global business, it has become synonymous with ongoing, never-ending progress. Kaizen is a strategy and cultural approach in which all employees—at every level of an organization—work proactively and collaboratively to improve processes, systems, and activities on an ongoing basis. Contrasting with top-down or radical reforms, Kaizen emphasizes bottom-up engagement: improvements are often suggested, tested, and refined by the frontline workers and teams who know their processes best. Core principles of Kaizen include:
Kaizen gained worldwide prominence through its systematic application at Toyota in the 1950s, where it became core to the company's lean manufacturing philosophy, emphasizing the reduction of waste, boosting productivity, and engaging employees to continuously improve quality and value. Over time, Kaizen has expanded beyond manufacturing into healthcare, software, services, and even individual productivity, demonstrating its universal relevance and adaptability. Leading Theorist: Masaaki ImaiMasaaki Imai is universally recognized as the leading theorist and ambassador of Kaizen to the world outside Japan. Biography and Relationship to Kaizen:
Other Influences: Kaizen remains a universal methodology for achieving sustained excellence—anchored by participative improvement, rigorous problem solving, and an unwavering focus on developing people and processes together. Its spread beyond Japan owes much to Masaaki Imai’s role as its theorist, teacher, and global champion.
|
| |
| |
Quote: John Doerr - Venture Capitalist“An effective goal-setting system starts with disciplined thinking at the top, with leaders who invest the time and energy to choose what counts.” — John Doerr, Measure What MattersThis insight from John Doerr encapsulates the transformative power of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) as a leadership discipline. Doerr emphasizes that meaningful organizational progress doesn’t begin with broad intentions or scattered efforts but with top leadership committing to carefully define, prioritize, and communicate the few goals that truly matter. Doerr’s central message to Google was: Strategy requires ruthless clarity—leaders must devote “time and energy to choose what counts,” setting focused objectives and quantifiable results. This disciplined approach allowed Google, and countless organizations since, to achieve sustained alignment, transparency, and execution at scale. About John DoerrJohn Doerr (b. 1951) is one of Silicon Valley’s most influential venture capitalists and thought leaders. Early in his career, he joined Intel, where he learned directly from Andy Grove’s culture of rigorous, measurable management. At Kleiner Perkins, Doerr helped fund and build some of the world’s most consequential technology companies, including Google, Amazon, and Sun Microsystems. Beyond capital, Doerr contributed operational insight—most notably by importing Intel’s OKR system to Google just after its founding. His book, Measure What Matters, distils decades of experience, showing how OKRs drive performance, accountability, and innovation in organizations ranging from start-ups to global giants. Doerr continues to advocate for mission-driven leadership and data-driven management, focusing on climate and societal impact alongside business achievement. Leading Theorists on Goal Setting and MeasurementThe intellectual roots of Doerr's philosophy are grounded in the science and practice of management by objectives and the broader theory of performance measurement:
John Doerr’s conviction is clear: Organizational greatness hinges not just on vision but on the discipline of leaders to set, prioritize, and measure what truly matters. The OKR framework, built on the shoulders of the world’s leading management theorists, remains a catalyst for clarity, focus, and transformative achievement.
|
| |
| |
Stay up to date with the Global Advisors Whatsapp channel!Follow our Global Advisors Whatsapp channel to get updates and news! |
| |
| |
Term: LeanLean is a management philosophy and set of practices aimed at maximizing value for customers by systematically identifying and eliminating waste in organizational processes, particularly in manufacturing but now widely applied across many sectors. The lean approach is rooted in five core principles:
Waste in lean (known as muda in Japanese) refers to any activity that consumes resources but does not add value to the customer. Classic categories of waste include overproduction, waiting, transportation, excess processing, inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects. Beyond process efficiency, lean is also about empowering workers, fostering cross-functional collaboration, and embedding continuous improvement (kaizen) into the company culture. Key Theorist: James P. Womack The leading contemporary advocate and theorist of lean as a strategic management system is James P. Womack. Womack transformed the field by articulating and popularizing lean concepts globally. He is best known for co-authoring the seminal book The Machine That Changed the World (1990) and, with Daniel T. Jones, codifying the five lean principles that underpin modern lean practices. Biography and Relationship to Lean: Womack’s framework distilled the essence of lean into the five principles described above and provided a strategic roadmap for their application in manufacturing, services, healthcare, and beyond. His continued research, writing, and global education efforts have made him the most influential figure in the dissemination and application of lean management worldwide. Summary: Lean is a customer-focused management system for continuous improvement and waste elimination, guided by five core principles. James P. Womack is the most prominent lean theorist, whose research and advocacy helped define, codify, and globalize lean as a foundational approach to organizational excellence.
|
| |
| |
Quote: Lord Kelvin (William Thomson) - Physicist“When you can measure what you are speaking about, and express it in numbers, you know something about it; but when you cannot measure it...your knowledge is of a meagre and unsatisfactory kind.” - Lord Kelvin (William Thomson)This iconic statement, voiced by Lord Kelvin in the late 19th century during a lecture, elegantly captures the spirit of scientific inquiry in the industrial age. Its context lies at the intersection of theory and practice: scientists and engineers were wrestling with how to systematize knowledge and drive real technological progress. The British Empire, amid the Industrial Revolution, thrived on advances in physics, engineering, and telegraphy, demanding both rigorous theory and practical, measurable outcomes. Kelvin’s philosophy was revolutionary for his time. He argued that true understanding comes not simply from speculation or qualitative insight but must be backed by quantitative measurement. This perspective helped establish the foundation for modern scientific method and engineering practice, where empirical data and precision are paramount. About Lord KelvinWilliam Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907) was a towering figure in science and engineering. Born in Belfast and educated at Cambridge, Kelvin held the chair of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for over half a century. His scholarship ranged from mathematical physics to practical engineering, and the breadth of his impact was remarkable:
In 1892, he was elevated to the peerage as Lord Kelvin, the first scientist to be so honoured, choosing his title after the River Kelvin that flows by the University of Glasgow. Leading Theorists and the Science of MeasurementLord Kelvin’s dictum on measurement shaped the work of generations of physicists, engineers, and organizational theorists. Measurement became the keystone of operational science, influencing leading minds far beyond physics:
Together, these theorists built on Kelvin’s insight that measurement is not mere accounting—it is the bedrock of progress in science, engineering, and organizational strategy. The enduring impact of this idea is visible in everything from physics and engineering to business analytics and modern performance management.
|
| |
| |
Term: OKRs - Objectives and Key ResultsOKR (Objectives and Key Results) is a widely used goal-setting framework that enables organizations, teams, and individuals to define clear, aspirational objectives and track their achievement through specific, measurable key results. This approach is designed to bridge the gap between strategy and execution, ensuring that high-level organizational vision gets translated into actionable, quantifiable outcomes. An OKR consists of two main components:
Initiatives often supplement OKRs but are not required; these are the projects and actions taken to influence the achievement of the Key Results. OKRs promote transparency, alignment, and accountability across organizations. They are generally set at the company, team, or individual level and are revisited quarterly or monthly for review and scoring. OKRs vs. KPIs and the Balanced Scorecard
Leading Strategy Theorist Behind OKRs: Andy GroveAndrew S. Grove (1936–2016) is credited as the originator of the OKR framework. Born in Budapest, Hungary, Grove survived Nazi occupation and the Soviet invasion before fleeing to the United States in 1956. He earned a Ph.D. in chemical engineering from the University of California, Berkeley. At Intel, where he was one of the earliest employees and later served as CEO (1987–1998) and Chairman, Grove revolutionized both the company and wider management thinking. In his 1983 classic High Output Management, he documented the use of "iMBO" (Intel Management by Objectives), which provided the foundation for OKRs as they are practiced today. Grove believed that combining ambitious, qualitative objectives with specific, quantitative key results was critical for driving focus, alignment, and acceleration of progress within highly competitive, fast-changing industries. Grove’s methods directly influenced pioneers such as John Doerr, who brought OKRs to Google and played a key role in their widespread adoption in Silicon Valley and beyond. OKRs offer a flexible, transparent alternative or complement to KPIs and tools like the Balanced Scorecard, driving organizational alignment, agility, and focus—an approach rooted in Andy Grove’s philosophy of high performance through clear, measurable ambition.
|
| |
| |
Quote: Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton – creators of the Balanced Scorecard approach“Today's organisational value-creating activities are not captured in the tangible, fixed assets of the firm. Instead, value rests in the ideas of people scattered throughout the firm, in customer and supplier relationships, in databases of key information, and cultures of innovation and quality.” - Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton - creators of the Balanced Scorecard approachThis statement exemplifies a key shift in modern management thinking championed by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton. Historically, companies measured their worth by physical assets—machinery, buildings, inventory, and other tangible resources. However, by the late 20th century, breakthrough research and business transformations revealed that intangible factors—knowledge, innovation, relationships, and organizational culture—were often the real drivers of sustainable value and competitive advantage. Kaplan and Norton addressed this gap by developing the Balanced Scorecard in the early 1990s, arguing that traditional financial measures alone were insufficient to capture an organisation’s true value-creating processes. Their framework encouraged leaders to assess performance not just in terms of revenue and profit, but also through perspectives such as internal business processes, customer satisfaction, and—critically—the innovation and learning (or learning and growth) perspective. This emphasised how assets like employee expertise, informational capital, and organizational learning drive future performance and adaptability. The quote reflects their conviction that in the knowledge economy, ideas, relationships, and a culture of continuous improvement are at the core of lasting organizational value. Kaplan and Norton’s holistic perspective reshaped global management practices, making companies far more aware of the hidden, intangible strengths that sustain growth and excellence. About Kaplan and Norton: Theorists Shaping Strategy and Measurement Robert S. Kaplan is an influential American academic and Emeritus Professor at Harvard Business School. Trained as an engineer and economist, Kaplan’s early research revolutionised management accounting through innovations like Activity-Based Costing. His engagement with performance measurement deepened when he collaborated with David P. Norton. David P. Norton came from a background combining engineering, business, and consultancy, ultimately crafting a career as a management strategist and executive. Norton’s work translated academic insights into practical tools for organisations across sectors. In 1990, Kaplan and Norton undertook a pioneering research project into how organizations measure performance. Their collaboration resulted in the creation of the Balanced Scorecard—a system designed to link strategy formulation with execution, and to provide executives with a balanced view of their organisation’s progress. Rather than relying on isolated metrics, their model integrates four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and innovation & learning. This approach compels organisations to consider whether they can continually improve and create value, not just deliver short-term results. Over the years, Kaplan and Norton continued to evolve their ideas, expanding the Balanced Scorecard approach into broader theories of strategy maps and organisational alignment. Their joint work has had profound influence, helping leaders around the world realize that a company’s most valuable assets are often those you cannot see on a balance sheet, but that can be measured, nurtured, and leveraged to achieve enduring success.
|
| |
| |
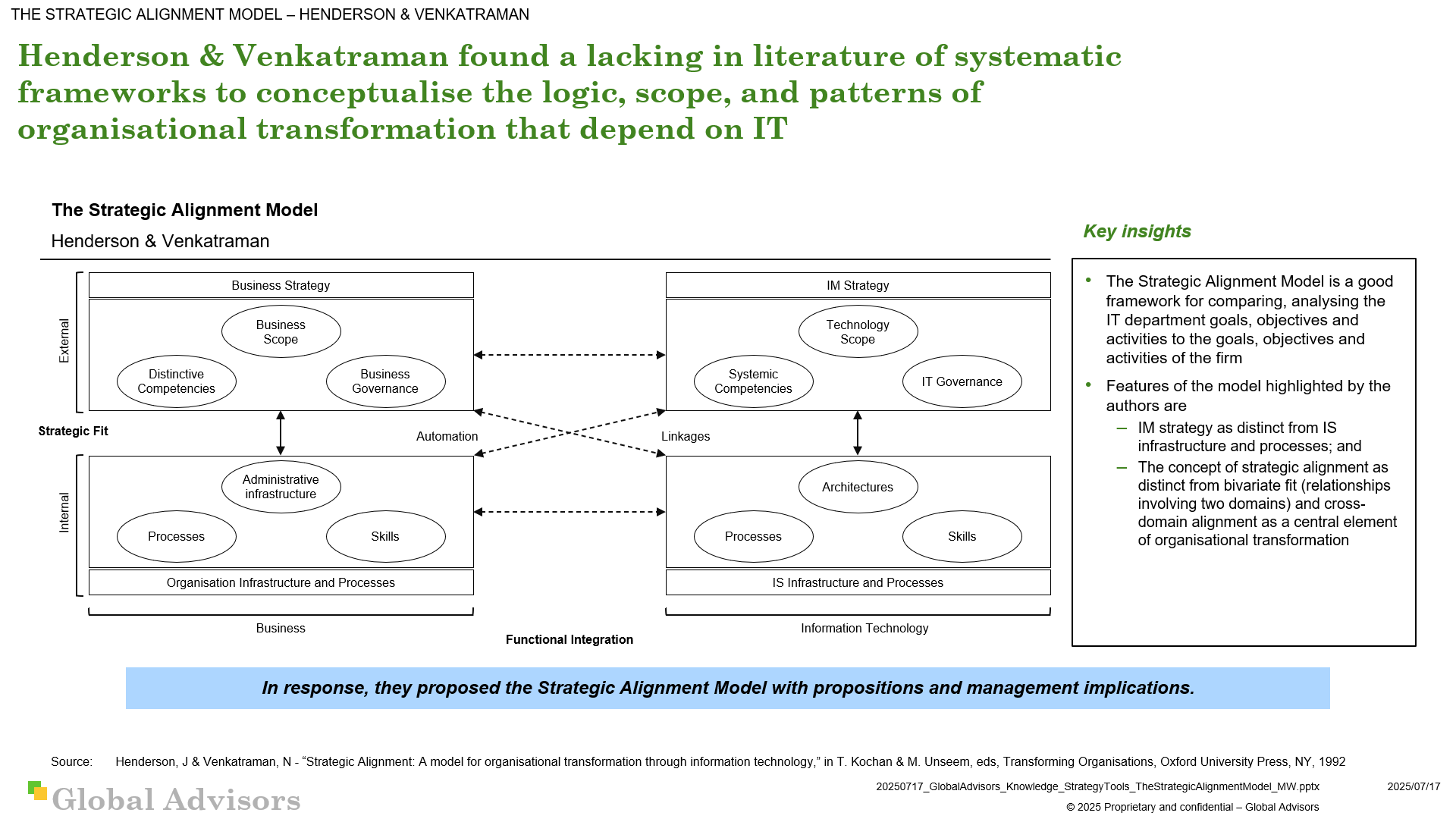
Term: Strategic Alignment ModelThe Strategic Alignment Model (SAM), as defined by Venkatraman and Henderson in the IBM Systems Journal, is a foundational framework for aligning an organization's business strategy and IM strategy to maximize value and achieve sustainable success.
The Strategic Alignment Model (SAM), as defined by Venkatraman and Henderson in the IBM Systems Journal, is a foundational framework for aligning an organization's business strategy and IT strategy to maximize value and achieve sustainable success. Core Components of the Strategic Alignment ModelThe model is structured around four domains—two external and two internal—each representing critical organizational dimensions:
Alignment occurs through two key linkages:
SAM proposes that achieving alignment requires choices across all four domains to be made in parallel, with consistent logic and rationale supporting both strategic formulation and execution. Perspectives on AlignmentVenkatraman and colleagues identify four dominant alignment perspectives for analytic alignment between Business and IT:
Each perspective highlights a different way in which business and IM strategies interact and shape organizational success. Key Theorists: N. Venkatraman and John C. HendersonN. Venkatraman is widely recognized as the principal architect behind the Strategic Alignment Model. His research in information technology, strategy, and organizational transformation helped establish the foundational link between IT investments and business value through effective alignment.
John C. Henderson collaborated extensively with Venkatraman and co-authored the original foundational work presenting the Strategic Alignment Model in the IBM Systems Journal.
Their relationship to the Strategic Alignment Model is that of co-originators. Their joint efforts have made SAM the dominant paradigm for addressing the alignment of business strategies and IT capabilities, profoundly influencing both theory and best practices in corporate strategy and digital transformation. In essence: The Strategic Alignment Model by Venkatraman and Henderson is the pivotal framework guiding organizations in aligning business and IT realms—represented and continuously refined by the scholarly work and deep expertise of these two leading theorists.
|
| |
| |
Quote: Fyodor Dostoevsky - Russian novelist, essayist and journalist"A man who lies to himself, and believes his own lies becomes unable to recognize truth, either in himself or in anyone else, and he ends up losing respect for himself and for others. When he has no respect for anyone, he can no longer love, and, in order to divert himself, having no love in him, he yields to his impulses, indulges in the lowest forms of pleasure, and behaves in the end like an animal. And it all comes from lying - lying to others and to yourself." - Fyodor Dostoevsky - Russian novelist, essayist and journalistFyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (November 11, 1821 – February 9, 1881) was a Russian novelist, essayist, and journalist who explored the depths of the human psyche with unflinching honesty. Born in Moscow to a family of modest means, Dostoevsky’s early life was marked by the emotional distance of his parents and an eventual tragedy when his father was murdered. He trained as a military engineer but pursued literature with relentless ambition, achieving early success with novels such as Poor Folk and The Double. Dostoevsky’s life took a dramatic turn in 1849 when he was arrested for participating in a radical intellectual group. Sentenced to death, he faced a mock execution before his sentence was commuted to four years of hard labor in Siberia followed by military service. This harrowing experience, combined with his life among Russia’s poor, profoundly shaped his worldview and writing. His later years were marked by personal loss—the deaths of his first wife and his brother—and financial hardship, yet he produced some of literature’s greatest works during this time, including Crime and Punishment, The Idiot, Devils, and The Brothers Karamazov. Dostoevsky’s writings are celebrated for their psychological insight and existential depth. He scrutinized themes of morality, free will, faith, and the consequences of self-deception—topics that continue to resonate in philosophy, theology, and modern psychology. His funeral drew thousands, reflecting his status as a national hero and one of Russia’s most influential thinkers. Context of the QuoteThe quoted passage is widely attributed to Dostoevsky, most notably appearing in The Brothers Karamazov, his final and perhaps most philosophically ambitious novel. The novel, published in serial form shortly before his death, wrestles with questions of faith, doubt, and the consequences of living a lie. The quote is spoken by the Elder Zosima, a wise and compassionate monk in the novel. Zosima’s teachings in The Brothers Karamazov frequently address the dangers of self-deception and the importance of spiritual and moral honesty. In this passage, Dostoevsky is warning that lying to oneself is not merely a moral failing, but a fundamental corruption of perception and being. The progression—from dishonesty to self-deception, to the loss of respect for oneself and others, and ultimately to the decay of love and humanity—paints a stark picture of spiritual decline. This theme is central to Dostoevsky’s work: characters who deceive themselves often spiral into psychological and moral crises. Dostoevsky saw truth—even when painful—as a prerequisite for authentic living. His novels repeatedly show how lies, whether to oneself or others, lead to alienation, suffering, and a loss of authentic connection. Leading Theorists on Self-DeceptionWhile Dostoevsky is renowned in literature for his treatment of self-deception, the theme has also been explored by philosophers, psychologists, and sociologists. Below is a brief overview of leading theorists and their contributions: Philosophers
Psychologists
Modern Thinkers
Legacy and InsightDostoevsky’s insights into the dangers of self-deception remain remarkably relevant today. His work, together with that of philosophers and psychologists, invites reflection on the necessity of honesty—not just to others, but to oneself—for psychological health and authentic living. The consequences of failing this honesty, as Dostoevsky depicts, are not merely moral, but existential: they impact our ability to respect, love, and ultimately, to live fully human lives. By placing this quote in context, we see not only the literary brilliance of Dostoevsky but also the enduring wisdom of his diagnosis of the human condition—a call to self-awareness that echoes through generations and disciplines.
|
| |
| |
|
| |
| |